Arduino Interfacing LED
LED Blinking Using Arduino
We will interface an LED (light-emitting diode) to the Arduino UNO board. An LED is a simple diode that emits light in a forward bias. We will write an LED-blinking program on the Arduino IDE and download it to the microcontroller board. The program simply turns ON and OFF LED with some delay between them.
Table of Content
What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source, board that has a Microchip ATmega328P microcontroller on it. This microcontroller has a set of Digital & Analog input and output pins. The operating voltage of the board is 5V. It has 14 digital I/O pins & 6 Analog input pins. The clock frequency of the microcontroller is 16 MHz.
What is LED?
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are becoming increasingly popular among a wide range of people. When a voltage is given to a PN Junction Diode, electrons, and holes recombine in the PN Junction and release energy in the form of light (Photons). An LED’s electrical sign is comparable to that of a PN Junction Diode. When free electrons in the conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band in forward bias, energy is released in the form of light.
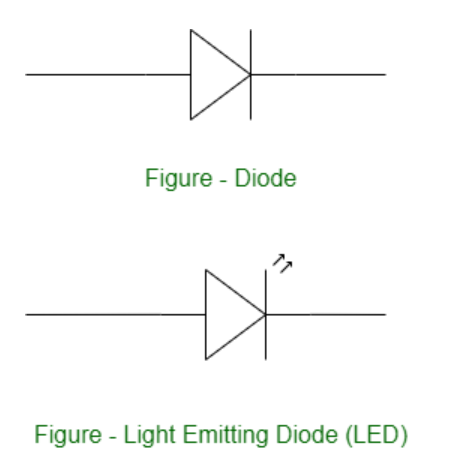
Structure of an LED
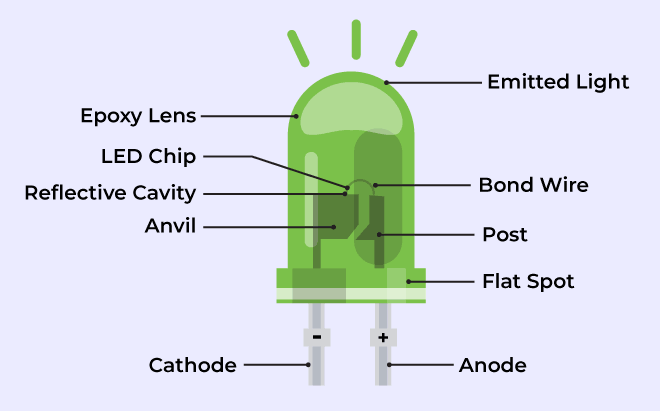
Structure of LED
The flow of charge carriers (electrons and holes) across the P-N junction drives the activity of an LED. When a forward voltage (anode positive in comparison to the cathode) is applied, electrons and holes recombine at the junction, releasing energy in the form of photons (light). The semiconductor chip is linked to external terminals known as the anode (+) and the cathode (-). The anode is linked to the P-region, and the cathode to the N-region.
Blinking an LED
Blinking an LED is an introductory Arduino project in which we control an LED using Arduino. LED blinking refers to the process of continuously turning an LED (Light Emitting Diode) and off in a repetitive pattern. It is a simple and common demonstration in electronics and microcontroller-based projects.
Working Procedure
setup() and loop() are two fundamental Arduino functions for controlling the behavior of your board. The Arduino framework automatically calls these functions, which form the foundation of any Arduino program.
The setup() function is only called once when the Arduino board boots up or is reset. Its goal is to set pin modes, initialize variables, and execute any other necessary setup tasks before the main loop begins. This function can be used to configure settings that should only be changed once over the board’s lifespan.
The loop() function is the heart of an Arduino program. After the setup() function is executed, the loop() function starts running repeatedly until the Arduino is powered off or reset. It contains the main code that performs the desired tasks, controls the board, user input. Whatever is included in the loop() function will be executed in a continuous loop, allowing the Arduino to perform its intended functions continuously.
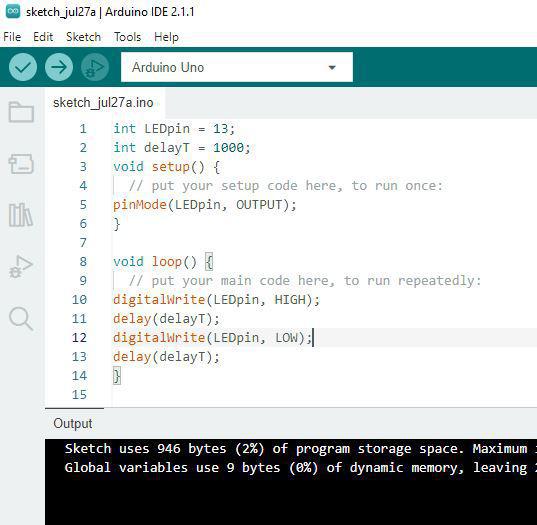
In the code, we have declared two integers, LEDpin and delayT. LEDpin represents the pin number of the Arduino where LEDs need to be connected, and delayT is an integer variable for the delay() function. The delay() function accepts values in milliseconds.
Components Required
- 1 X LED
- 1 X Resistor, 330 Ohm
- Breadboard
- Arduino UNO R4 or earlier versions.
- Jumper wires
Components Description
- 1 X LED: We are controlling only one LED in this program.
- 1 X Resistor, 330 Ohm: For every LED, we need one current limiting resistor.
- Breadboard: A breadboard is a fundamental tool used in electronics and prototyping to build and test circuits without soldering.
- Arduino UNO R4 or earlier versions.
- Jumper wires: Jumper wires are simple electrical wires with connectors on both ends used to create connections between various electronic components or points on a circuit on a breadboard.
Arduino Code
int LEDpin = 13;
int delayT = 1000;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(LEDpin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
digitalWrite(LEDpin, HIGH);
delay(delayT);
digitalWrite(LEDpin, LOW);
delay(delayT);
}
Deployment Using Arduino IDE
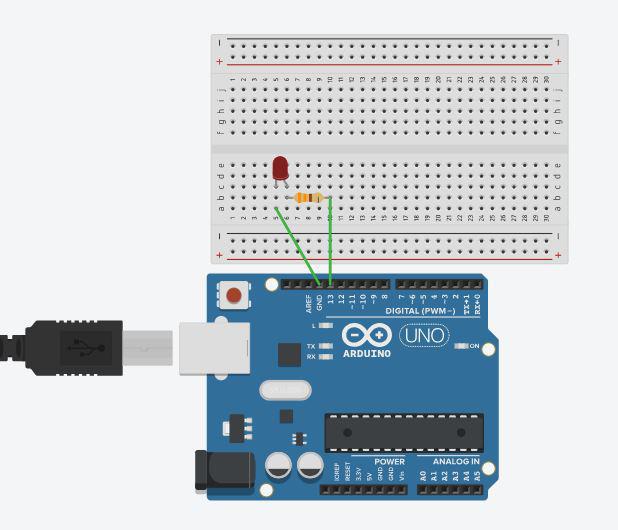
Circuit Diagram
In the circuit diagram, we used one 330-ohm resistor in series with the LED. This resistor is also called a current-limiting resistor. The Anode of the LED (the longer pin) is connected to one end of the resistor, and the cathode (the shorter pin) is connected to the ground. The other end of the resistor is connected to the Arduino pin. A step-by-step explanation is as follows:
- LED Connections: Connect the LED to the breadboard. The LED has two legs, the longer of which is the anode (positive) and the shorter of which is the cathode (negative).
- Resistor Connection: Insert one end of the resistor into the same row of the breadboard as the LED’s Anode. The resistor’s other end should be connected to the Arduino’s digital output pin.
- Ground (GND) Connection: Connect a jumper wire from the same row as the LED’s cathode to any Arduino board GND (Ground) pin. This connects the circuit to the ground of the Arduino.
The circuit is now complete. Here’s how it works:
When you upload a simple Arduino program that controls the LED, the microcontroller on the Arduino board executes the program, and the LED will blink according to the code you wrote.
Applications and Uses of LED Blinking
The LED blinking project is an important and straightforward method that can be utilized for a wide range of applications in microcontroller-based projects like :
- Security Systems: To check the status of security systems
- Warning Signals: In battery-operated devices, LED blinking can be used to indicate low battery levels.
- In Testing and debugging.
- Status Indication: LEDs can be used to indicate different states of a system. For example, in a home automation project, an LED might blink to indicate whether a device is connected to an internet network or not.
Conclusion
The Arduino LED blinking project provides a hands-on introduction to microcontrollers, hardware interfaces, and programming ideas. It serves as a foundation for more sophisticated projects and allows you to experiment with numerous Arduino features and capabilities. Whether you’re new to electronics or an expert maker, this project will help you develop crucial skills and knowledge for future Arduino-based projects.
Digital Thermometer using Arduino and LM35 Temperature Sensor

Thermometers are useful apparatus being used since long time for temperature measurement. In this project we have made an Arduino based digital thermometer to display the current ambient temperature on a 16x2 LCD unit in real time . It can be deployed in houses, offices, industries etc. to measure the temperature. We can divide this Arduino based thermometer into three sections - The first section senses the temperature by using temperature sensor LM35, second section converts the temperature value into a suitable numbers in Celsius scale which is done by Arduino, and last part of system displays temperature on 16x2 LCD. The same is demonstrated in below block diagram.
In this digital temperature sensor with Arduino, Arduino Uno is used to control the whole process. An LM35 temperature sensor is used for sensing environment temperature which gives 1 degree temperature on every 10mV change at its output pin. You can easily check it with voltmeter by connecting Vcc at pin 1 and Ground at pin 3 and output voltage at pin 2 of LM35 sensor. For an example if the output voltage of LM35 sensor is 250m volt, that means the temperature is around 25 degree Celsius.
Arduino reads output voltage of temperature sensor by using Analog pin A0 and performs the calculation to convert this Analog value to a digital value of current temperature. After calculations arduino sends these calculations or temperature to 16x2 LCD unit by using appropriate commands of LCD. We have also built other digital thermometer projects using DHT11, DS18B20 and other temperature sensors.
Circuit Components
Arduino
In this project we have used a Arduino to control whole the process of system. Arduino is a controller which runs on ATmega AVR controller. Arduino is an open source hardware platform and very useful for project development purpose. There are many types of Arduino boards like Arduino UNO, arduino mega, arduino pro mini, Lilypad etc. available in the market or you can also build Arduino by yourself.

LM35 Temperature Sensor
LM35 is a 3 pin temperature sensor which gives 1 degree Celsius on every 10mVolt change. This sensor can sense up to 150 degree Celsius temperature. 1 number pin of lm35 sensor is Vcc, second is output and third one is Ground. LM35 is the most simplest temperature sensor and can be interfaced easily with any microcontroller. You can check various Temperature Measurement using LM35 based projects here.
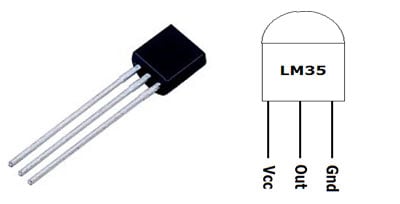
Pin No | Function | Name |
1 | Supply voltage; 5V (+35V to -2V) | Vcc |
2 | Output voltage (+6V to -1V) | Output |
3 | Ground (0V) | Ground |
LM35 can be easily interfaced with Raspberry Pi, NodeMCU, PIC microcontroller, etc to measure the temperature and can also be used standalone with Op-amp to indicate temperature levels.
LCD
16x2 LCD unit is widely using in embedded system projects because it is cheap, easily availablet, small in size and easy to interface. 16x2 have two rows and 16 columns, which means it consist 16 blocks of 5x8 dots. 16 pin for connections in which 8 data bits D0-D7 and 3 control bits namely RS, RW and EN. Rest of pins are used for supply, brightness control and for backlight.

Power Supply
Arduino Board already have an inbuilt power supply section. Here we only need to connect a 9 volt or 12 volt adaptors with the board.
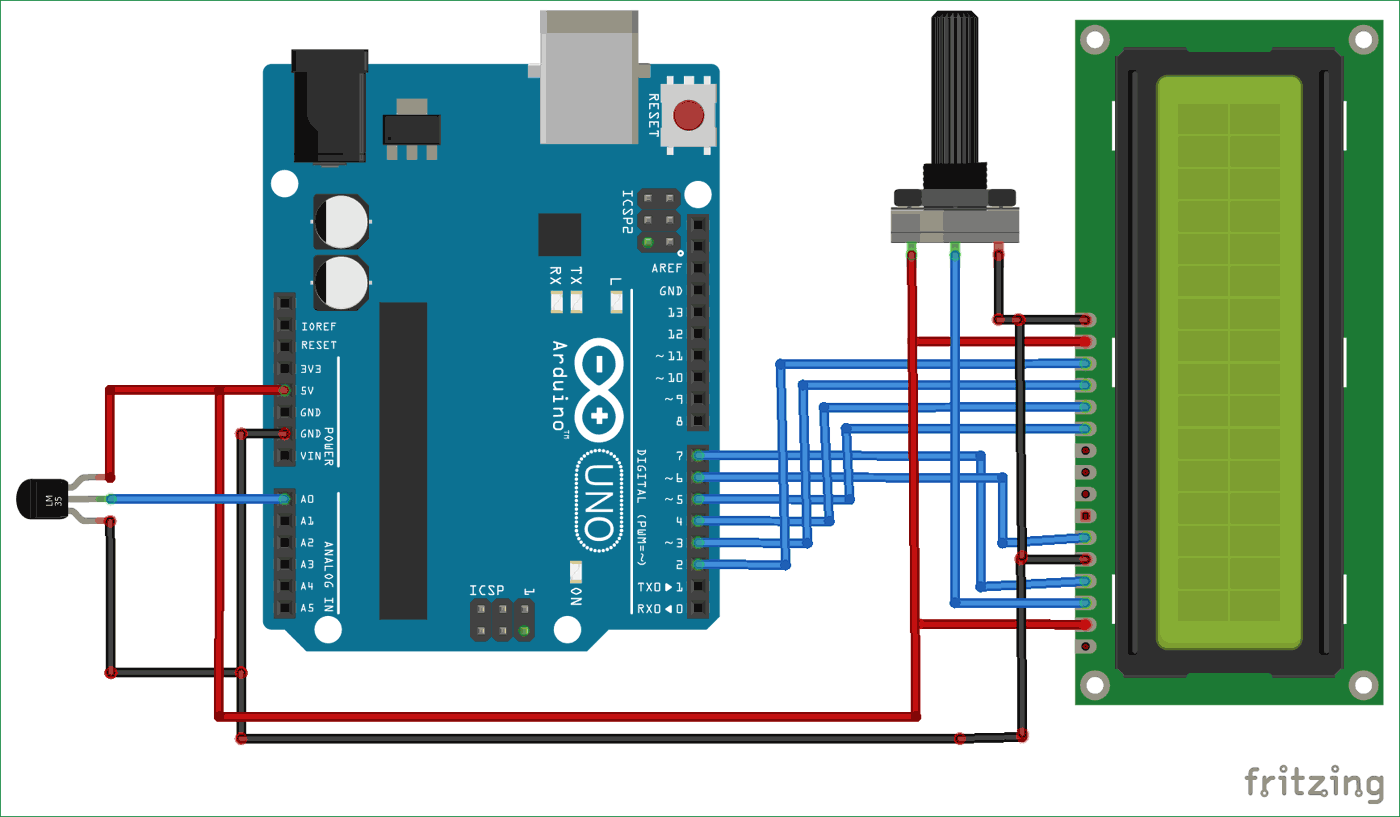
Circuit Diagram and Explanation
Circuit digram for Digital Thermometer using Arduino and LM35 Temperature Sensor, is shown in the above figure. Make the connections carefully as shown in the schematic. Here 16x2 LCD unit is directly connected to arduino in 4-bit mode. Data pins of LCD namely RS, EN, D4, D5, D6, D7 are connected to arduino digital pin number 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2. A temperature sensor LM35 is connected to Analog pin A0 of arduino, which generates 1 degree Celsius temperature on every 10mV output change at its output pin.
If you are new to Arduino then learn to interface 16x2 LCD with Arduino in our previous tutorial.
Arduino LM35 Code & Explanation
The code for Temperature Measurement using LM35 is simple and given at the end of this tutorial. First we include library for LCD unit and then we defines data and control pins for LCD and temperature sensor.
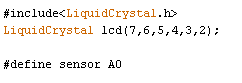
After getting analog value at analog pin we reads that value using Analog read function and stores that value in a variable. And then convert the value into temperature by applying the below given formula.
Comments
Post a Comment